Obtain news and background information about sealing technology, get in touch with innovative products – subscribe to the free e-mail newsletter.

10.10.2017 | Story
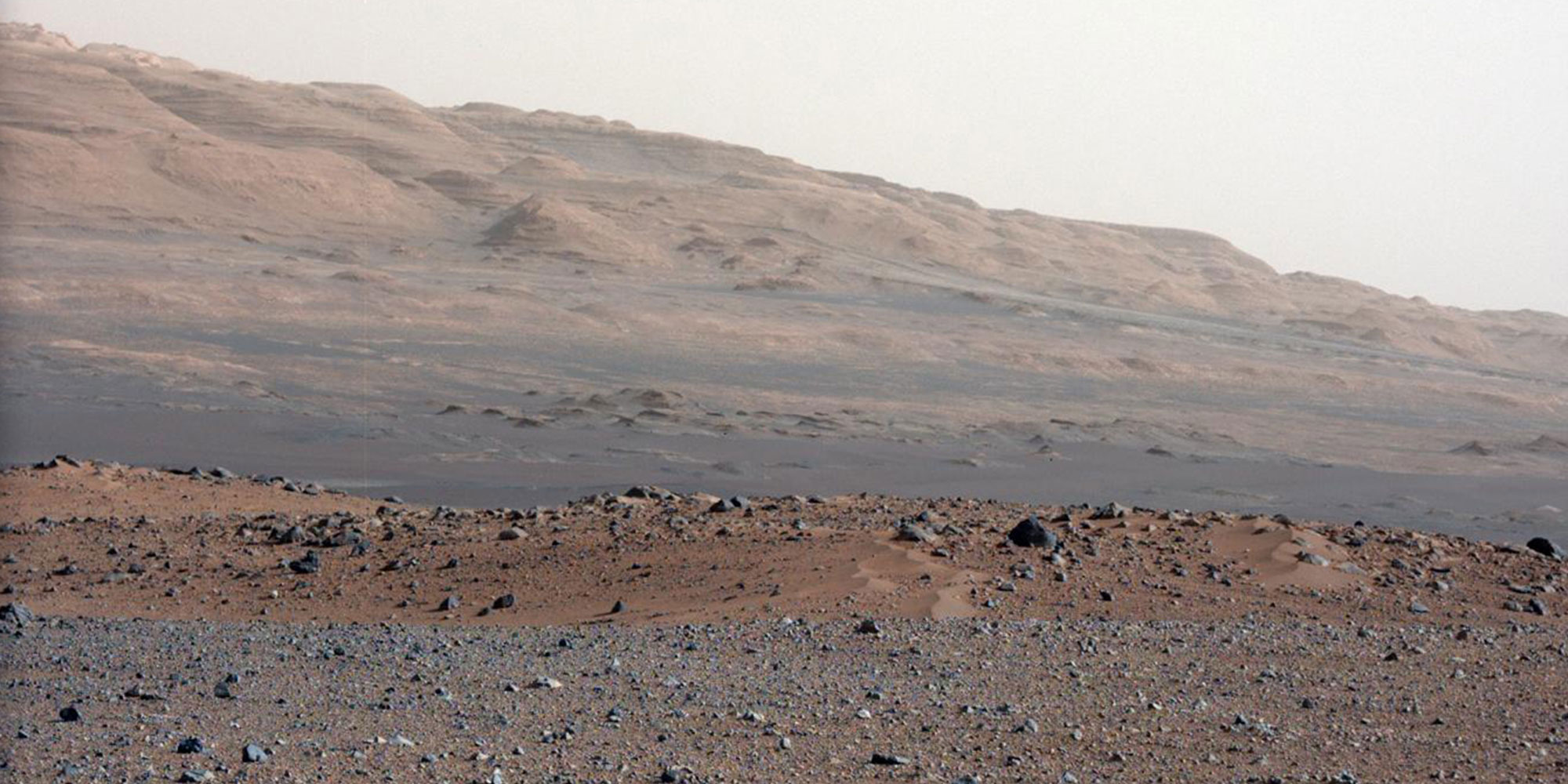
Sights Set on Mars
When spaceflight was still new in the 1960s, the moon was the destination. Fifty years later, humanity is focusing on Mars. The goal is not just to visit the planet. At some point, it is expected to be inhabited long-term.
Why Mars of All Places?
Yet there is something about Mars that makes it appealing. It is considered to be uncommonly rich in resources. Gravity on Mars is not as strong as it is on Earth, making heavy objects easier to move. And then there is the fact that the Martian day approximates the 24 hours to which humans are accustomed. And above all else, the trip to Mars is no longer considered the challenge. Depending on the configuration of the planets, it can be reached in about six months. What is galvanizing researchers is the fact that there is water in frozen form on the red planet. If Mars could be heated up, the ice would melt, making the planet a bit more livable.

Wanted: A Greenhouse Effect
NASA has gone as far as contemplating the use of a bipolar magnetic field to warm the planet. Once it was positioned between Mars and the sun, the planet would be protected and in a position to independently rebuild its atmosphere. On the lee side of the magnetic field, a kind of greenhouse effect would establish itself and would lead to warmer temperatures. This would allow the already available carbon dioxide to rise and the atmosphere to become increasingly dense. Mars would be on the way to becoming a little greener, even if the process were endlessly slow.
Construction Materials at Hand
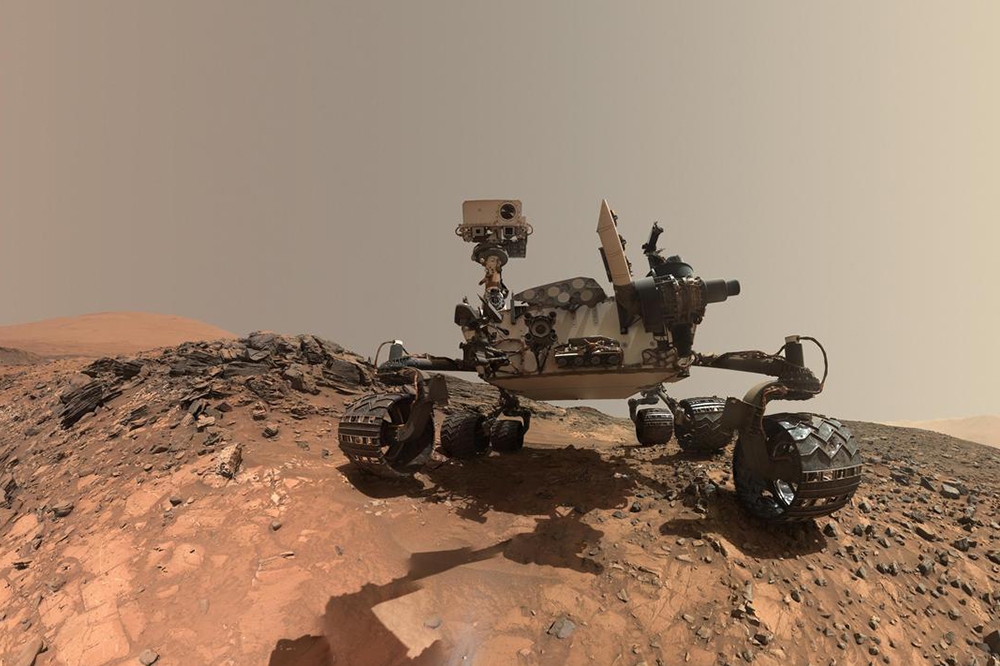
While the construction of a magnetic shield in space is nothing more than an intellectual game whose feasibility is highly contested, other NASA researchers are dealing with living and surviving on Mars in the short term. An infrastructure on site, including landing sites, hangars and living spaces shielded from radiation, would be urgently needed for this. But how are the materials for this supposed to be transported from the Earth to Mars, when every kilogram transported into space is tied to increased costs? But that’s not the case. Instead, the plan is to use the material available on site. Astronauts would not have to do the work. Instead, it would be done by autonomously operating 3D printers that draw their energy from the sun. Robots would mine the construction material and bring it to the printer.
Good Results from the 3D Printing Competition
NASA is already testing the manufacture of habitats in real life. In August 2017, they had three teams compete against one another in a competition. Using 3D printing, the contest demonstrated how stable living spaces on a small scale could be manufactured with materials similar to those found on Mars. The results impressed the researchers. So perhaps in the foreseeable future, space travelers could indeed establish themselves at least temporarily in settlements on Mars. The will to do so already exists, and the time for the departure is getting closer.
For the November edition of the customer magazine ESSENTIAL, we spoke with a Mars expert from NASA about the colonization of the planet and the crucial role falling to 3D printing. Stay tuned for the edition entitled “Departure.”
NASA generously made the image material available.
More news on the subject Technology & Innovation

First Hand News
Best of all, keep up with the latest developments
with the Freudenberg Sealing Technologies newsletter.