Obtain news and background information about sealing technology, get in touch with innovative products – subscribe to the free e-mail newsletter.
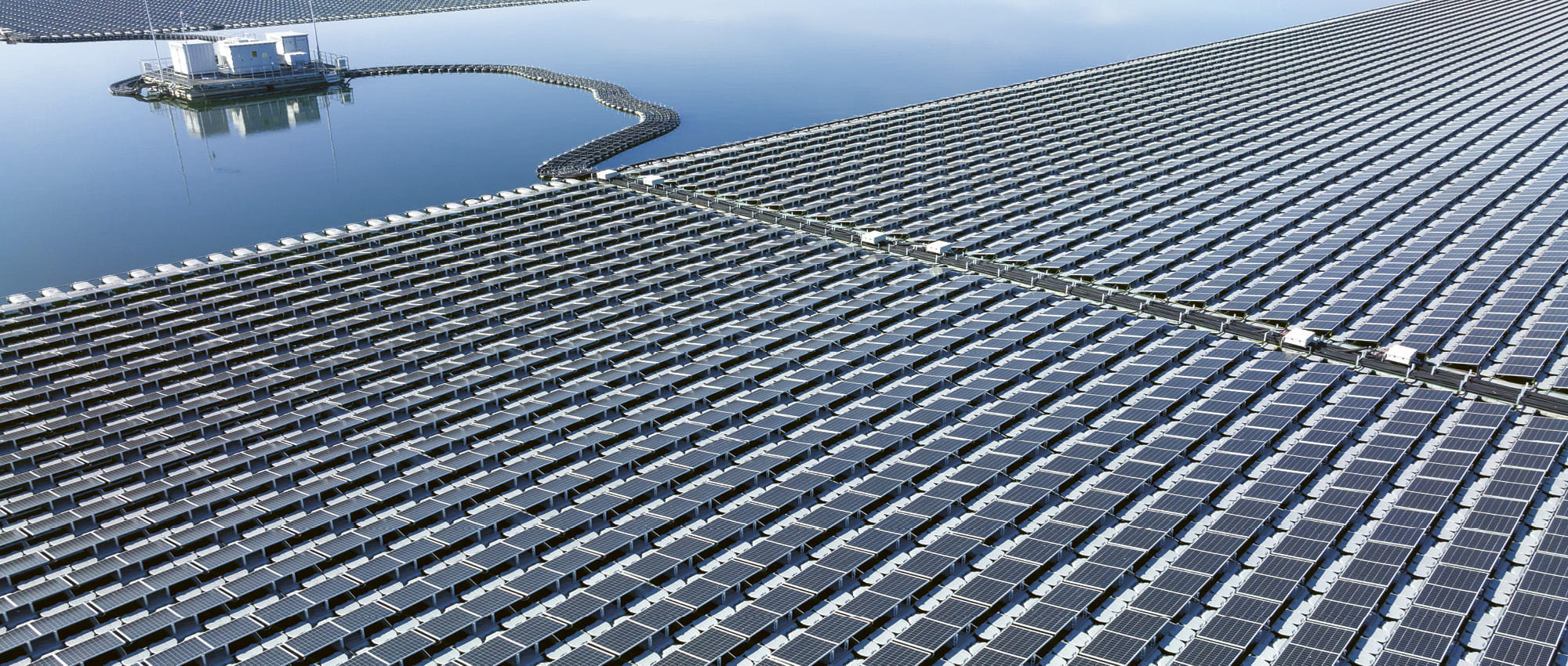

A Photovoltaic-Hydropower Hybrid
The Thai sun shines down on millions of tourists every year. It simultaneously generates large amounts of electricity. Thailand is currently home to the world’s largest hydro-solar park.
Sunshine, water and solar cells. Visitors to the Sirindhorn reservoir in Thailand see a huge, floating photovoltaic system about the size of 70 football fields. A walkway with panoramic views and souvenir shops highlights the importance of tourism to Thailand. But the Sirindhorn reservoir is more than a travel attraction. It is currently the world’s largest hybrid-solar park.
Photovoltaics as Far as the Eye Can See
The very name of the power plant highlights its special feature: Hydropower and solar energy have combined their forces. The facility taps into two sources of energy at one location. It is also more stable when weather conditions change. The solar cells mainly produce energy during the day, while the hydroelectric turbines meet the demand at night. Furthermore, the photovoltaic panels leave part of the lake in shade, reducing evaporation. If there are long periods of hot weather, the system can compensate for low water levels and the corresponding decline in hydropower output.
That is an important advantage since Thailand is increasingly grappling with extreme weather conditions and the impact of climate change. In April, temperatures rose to 45°C (113°F), breaking records. Officials warned people not to leave their homes. Thailand is not alone. Exceptionally high temperatures, accompanied by heat-related deaths, were recorded in the entire region as well as in China and India. These conditions are not only harmful for people and nature – they cause the demand for electricity to soar as air conditioners and other appliances run full blast. Efficient sources of energy are in greater demand than ever.
High Output from a Small Space
The Sirindhorn dam has faithfully served Ubon Ratchathani province for more than 60 years; the reservoir is the largest in the region. Its electrical output flows into the domestic market. The floating solar cells boosted capacity to 45 megawatts in 2021 – without taking up additional land. The photovoltaic park takes up relatively little space since the solar modules cover barely 1 percent of the lake’s surface. According to the public electrical utility, that leaves plenty of space for the ecosystem and a local fishery.
The Special Effect of Solar Cells on Water
The solar modules are designed to be as environmentally friendly as possible. Their floating substructure is made of a special plastic that is resistant to ultraviolet light. That means the high-density polyethylene does not decompose, thus preventing more microplastics from harming the underwater world. The floating solar cell’s greatest contribution is its capacity. The systems sit high on the water, and the cool environment boosts their electrical output up to 10 percent higher than land-based solar power systems. There are also no buildings around casting shadows on the panels. But floating power plants do have a weakness: They are relatively complicated and expensive to install. So, it is recommended that hydropower plants with reservoirs be retrofitted with them to take advantage of the existing infrastructure and connection to the grid. This was the approach taken at the Sirindhorn reservoir.
Floating Gigawatt Projects for Southeast Asia
Sunlight, water and solar modules – hydro-solar plants are a promising energy solution for sundrenched countries. It is no accident that Thailand is planning to build other hybrid plants – 15 of them at this point. By the year 2037, a total capacity of 2.7 gigawatts should be available. The country’s neighbors have been paying attention for a while: In nearly every ASEAN country, projects are underway in the three-digit megawatt – or even gigawatt – range. Southeast Asia plans to use its combination of water and sunlight for more than just tourism and agriculture.
This article originally appeared in ESSENTIAL, Freudenberg Sealing Technologies’ corporate magazine that covers trends, industries and new ideas. To read more stories like this, click here.
More Stories About Sustainability

Join Us!
Experience Freudenberg Sealing Technologies, its products and service offerings in text and videos, network with colleagues and stakeholders, and make valuable business contacts.
Connect on LinkedIn! open_in_new